写在开头
iOS开发这么久,接触和使用底层runtime也不止一次了,也总是没有去好好的系统研究一番~
总是很好奇,去试着学习,发现,创造~
前言
Objective-C是一门动态的语言,而Runtime铸就了它动态语言的特性。
深入
在苹果的官方文档Objective-C Runtime Programming Guide是这样组织的:

那么从messaging说起
恩,这点很重要,Objective-C根据Smalltalk发展而来,而Alan Kay(smalltalk核心开发成员)多次强调消息传递(message-passing)是Smalltalk重要的部分。
In Objective-C,The compiler converts a message expression into a call on a messaging function, objc_msgSend.
//
[receiver message]
//
objc_msgSend(receiver, selector)
//
objc_msgSend(receiver, selector, arg1, arg2, ...)
消息传递的关键在于两个重要的因素:
-
objc_object中的isa point
This pointer, called isa, gives the object access to its class and, through the class, to all the classes it inherits from. -
objc_class中的 class dispatch table
This table has entries that associate method selectors with the class-specific addresses of the methods they identify.
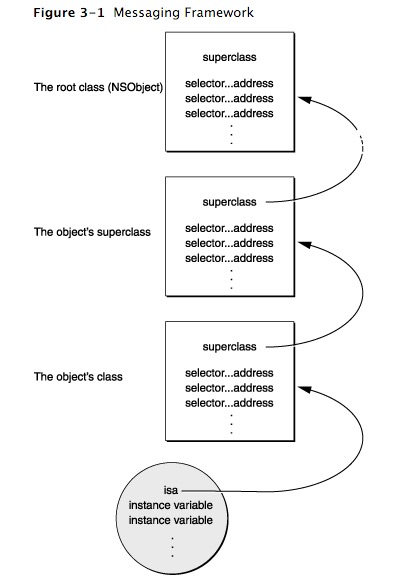
相关描述。。。
那么在底层整个过程是怎样的呢? 底层的结构是如何定义的呢?
/// A pointer to an instance of a class.
typedef struct objc_object *id;
/// Represents an instance of a class.
struct objc_object {
Class isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY;
};
/// An opaque type that represents an Objective-C class.
typedef struct objc_class *Class;
///
struct objc_class {
Class isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY;
#if !__OBJC2__
Class super_class OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
const char *name OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
long version OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
long info OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
long instance_size OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
struct objc_ivar_list *ivars OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
struct objc_method_list **methodLists OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
struct objc_cache *cache OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
struct objc_protocol_list *protocols OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
#endif
} OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
/// An opaque type that represents a method selector.
typedef struct objc_selector *SEL;
/// A pointer to the function of a method implementation.
#if !OBJC_OLD_DISPATCH_PROTOTYPES
typedef void (*IMP)(void /* id, SEL, ... */ );
#else
typedef id (*IMP)(id, SEL, ...);
#endif
objc_msgSend(reciver,foo)调用时,查找SEL的IML的过程如下:
- 通过 reciver 的 isa 指针找到它的 class
- 在 class 的 method list 找 foo
- 如果 class 中没到
foo,继续往它的 superclass 中找 - 一旦找到
foo这个函数,就去执行它的实现IMP
那么问题来了,如果foo未找到呢?系统又是如何处理的?
苹果处理未找到方法的过程如下:

从图上看出主要有三个步骤:
- Dynamic Method Resolution
我们可以通过resolveInstanceMethod:andresolveClassMethod:给一个实例方法或者类方法提供动态实现。
given the following function:
void dynamicMethodIMP(id self, SEL _cmd) {
// implementation ....
}
we can dynamically add it to a class as a method (called resolveThisMethodDynamically) using resolveInstanceMethod: like this:
@implementation MyClass
+ (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)aSEL
{
if (aSEL == @selector(resolveThisMethodDynamically)) {
class_addMethod([self class], aSEL, (IMP) dynamicMethodIMP, "v@:");
return YES;
}
return [super resolveInstanceMethod:aSEL];
}
@end
- forwardingTargetForSelector
如果目标对象实现了forwardingTargetForSelector:,Runtime 就会调用这个方法,把这个消息转发给其他对象。
- (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector
{
if(aSelector == @selector(mysteriousMethod:)){
return alternateObject;
}
return [super forwardingTargetForSelector:aSelector];
}
-
forwardInvocation
If you send a message to an object that does not handle that message, before announcing an error the runtime sends the object aforwardInvocation:message with anNSInvocationobject as its sole argument—theNSInvocationobject encapsulates the original message and the arguments that were passed with it.You can implement a
forwardInvocation:method to give a default response to the message, or to avoid the error in some other way. As its name implies,forwardInvocation:is commonly used to forward the message to another object.
- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation
{
if ([someOtherObject respondsToSelector:
[anInvocation selector]])
[anInvocation invokeWithTarget:someOtherObject];
else
[super forwardInvocation:anInvocation];
}
– 那么可以总结如下:
- 如果没有找到,Runtime 会发送 +resolveInstanceMethod: 或者 +resolveClassMethod: 尝试去 resolve 这个消息
- 如果 resolve 方法返回 NO,Runtime 就发送 -forwardingTargetForSelector: 允许你把这个消息转发给另一个对象
- 如果没有新的目标对象返回, Runtime 就会发送 -methodSignatureForSelector: 和 -forwardInvocation: 消息。你可以发送 -invokeWithTarget: 消息来手动转发消息或者发送 -doesNotRecognizeSelector: 抛出异常
–
写在最后
补充
- Objective-C RunTime是开源的。源代码:http://www.opensource.apple.com/source/objc4/
参考文章
https://developer.apple.com/library/ios/documentation/Cocoa/Conceptual/ObjCRuntimeGuide/Introduction/Introduction.html#//apple_ref/doc/uid/TP40008048-CH1-SW1
http://tech.glowing.com/cn/objective-c-runtime/
http://zhangbuhuai.com/2015/04/27/unstanding-the-Objective-C-Runtime-part3/
http://cocoasamurai.blogspot.sg/2010/01/understanding-objective-c-runtime.html
